Wang Wei, Doctor, from the School of Textile Garment and Design recently published the paper entitled "Advances in recyclable and superior photocatalytic fibers: Material, construction, application and future perspective" in the International renowned jou
Wang Wei, Doctor, from the School of Textile Garment and Design recently published the paper entitled "Advances in recyclable and superior photocatalytic fibers: Material, construction, application and future perspective" in the internationally renowned journal "Composites Part B: Engineering" (Area of SCI Division, Chinese Academy of Sciences, IF = 7.635) with the first author and Changshu Institute of Technology as the first completion unit.
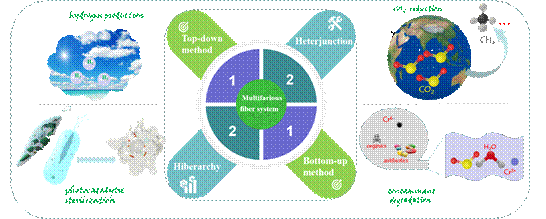
Scheme 1. Illustration of preparation and designed methods for photocatalytic fiber systems and their applications. Number 1 represents the group of synthesis methods; Number 2 represents the microstructure types; Benefited from the designed architecture, which is controlled by specific method, photocatalytic fiber systems exhibit broad applications in contaminant removal, photocatalytic sterilization, hydrogen production and CO2 reduction owing to the large specific areas, plenty of active sites and efficient transfer rate of charge carriers.
Photocatalytic fibers, with their excellent photocatalytic activity, porous structure, outstanding recyclability and deformability, are regarded as one of the most robust and proficient material supplies available for environmental remediation and energy conversion. However, there are few comprehensive reviews on this subject with high photocatalytic activity. In this paper, the latest explosive progress on photocatalytic fibers was analyzed, with regard to multifarious fiber substrate, design philosophy and general construction approaches. Upon matched band gap alignment, hierarchical structure, multicomponent coupling and surface hydrophilicity merits, the prominent features of these photocatalytic fibers were highlighted in the fields of pollutant removal, photocatalytic sterilization, hydrogen evolution and CO2 reduction. Meanwhile, their photocatalytic mechanisms of oxidation and reduction reactions were expounded as well as the radical species. Finally, the key challenges and perspectives for future advances were proposed with the aim of providing new insights for further improvement of photocatalytic fibers for applications through this review.
Access to Document: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2020.108512